Both Animal Fats And Plant Oils Are Examples Of What Monomer?
What are fats and oils?
Fats
Why does our torso need oils and fats?
- Source of free energy
Fats and oils serve every bit the most efficient means for living things to shop energy. They are thus an important source of energy. Like saccharide, fat releases energy when information technology is oxidised to carbon dioxide and water. They supply us with more free energy per gram than carbohydrates. - Source of nutrients
Nosotros need to include vitamins as office of a balanced diet to maintain practiced health. Vitamins A, D, E and K are insoluble in water but soluble in fats. We can meet our vitamin requirements by consuming foods that contain these fat-soluble vitamins. - Structural role
Fat plays important structural roles in the trunk. The protective membrane of each trunk jail cell is made from fat molecules. Even the nucleus of the prison cell is protected by layers of fatty molecules. - Thermal insulation
The layer of fat under our peel is to protect us from the cold and to protect our internal organs from freezing. The layer of fat under the skin acts as a thermal insulator. - Protection
Fat surrounds and protects vital internal organs in our trunk. For example, kidney is protected by a layer of fatty.
People also inquire
- What are carbon compounds?
- Chemical Backdrop of Carbon Compounds
- How are alkanes formed?
- What is an alkene in chemistry?
- What is an isomerism?
- What is booze and how is it made?
- How are carboxylic acids formed?
- How esters are formed?
- How palm oil is extracted?
- Society in Homologous Serial
- What is the monomer of natural rubber?
- Which acid is used for coagulating rubber from latex?
- Classification of Hydrocarbons
- What is the homologous serial of hydrocarbons?
- Properties and Uses of Ethanol
- Backdrop and Uses of Ethanoic Acrid
What are some examples of saturated and unsaturated fats?
Saturated and unsaturated fats
- The physical and chemic properties of a fat or oil molecule are greatly afflicted by the parent fatty acids. The fatty acids can be unlike in two main ways.
- Firstly, the length of the carbon chain tin can differ, ranging from 12 to 18 carbon atoms. For example, lauric acid (12 carbon atoms) and stearic acid (18 carbon atoms) have different numbers of carbon atoms.
- Secondly, the fatty acid may be saturated or unsaturated. A saturated fatty acid has all carbon atoms joined together by carbon-carbon unmarried bonds. Palmitic acid is a saturated fat acid.
- In an unsaturated fatty acid, the carbon chain has one or more than carbon-carbon double bonds. If the fatty acrid molecule has one carbon-carbon double bond, information technology is described as monounsaturated. Oleic acid is a monounsaturated fatty acid containing one carbon-carbon double bond.
- If there is more than one carbon-carbon double bail, the fatty acid is described as polyunsaturated. Linoleic acid has two carbon- carbon double bonds, whereas linolenic acid has three carbon-carbon double bonds.
The formulae of some fatty acids are given in Tabular array.
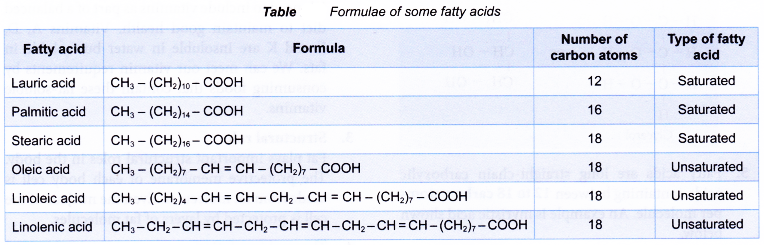
Table shows the composition of a few types of fats and oils.
| Source | Saturated fats (%) | Unsaturated fats (%) | |||||
| Myristic acid | Palmitic acid | Stearic acid | Others | Oleic acrid | Linoleic acid | Others | |
| Butter | 10 | 25 | 10 | 21 | 25 | five | 4 |
| Animal fats | 4 | 29 | nineteen | – | 44 | three | i |
| Groundnut oil | – | vii | 5 | – | 60 | 20 | viii |
| Olive oil | 1 | five | 5 | – | eighty | 7 | 2 |
| Palm oil | – | 44 | 5 | – | forty | ten | one |
Converting unsaturated fats to saturated fats
- Unsaturated fats can be converted into saturated fats by a procedure chosen catalytic hydrogenation. Each carbon-carbon double bail absorbs one mole of hydrogen.
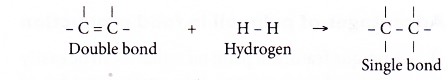
- The hydrogenation process is carried out by bubbling hydrogen gas through hot liquid oil in the presence of fine particles of nickel catalyst. A temperature of about 200°C and a pressure of well-nigh 4 atm are used.
- The relative molecular mass of the oil molecule increases, as more and more than of the double bonds are hydrogenated. Intermolecular forces become stronger and more free energy is needed to overcome them. The humid indicate of the oil increases and the physical land changes from liquid to solid.
- Margarine is a soft solid with low melting point at room temperature. It is made by hydrogenating some of the carbon-carbon double bonds in polyunsaturated vegetable oil such equally palm oil and sunflower oil.
How practise saturated and unsaturated fats affect the body?
Effect of fats on health
- Medical research has establish that a diet high in creature fats, specially saturated fats, is considered unhealthy.
(a) Fatty foods are very loftier in energy. 1 gram of fat releases most 9 kilocalories of energy. Hence, high consumption of nutrient high in fats and oils is likely to outcome in obesity.
(b) An obese person is prone to suffer from heart illness and other diseases such as diabetes. - Medical researchers have constitute that brute fats pose a greater risk for coronary heart disease and strokes than vegetable oils. Saturated fats contain cholesterol.
(a) Consuming food loftier in saturated fats will raise the level of cholesterol in the bloodstream. It is the cholesterol which causes fat deposits or plaque on the walls of veins or arteries. As the plaque builds up on the walls of the blood vessels, blood circulation is restricted and this will enhance blood pressure.
(b) Hardening of the arteries occurs if the deposits have place in the heart arteries. A condition called arteriosclerosis occurs, preventing acceptable supply of blood from reaching the heart and can cause centre attack.
(c) High-density lipoproteins (HDL) is called the 'practiced' cholesterol because it can reduce the risk of heart disease. Loftier levels of low-density lipoproteins (LDL), the 'bad' cholesterol, increase the risk of middle disease. - Vegetable oils do not contain cholesterol because only animals make cholesterol. These unsaturated fats do non have the damaging furnishings of saturated fats to cause cardiovascular problems. This does non mean that we can eat unsaturated fats in large quantities. Likewise much fat, whether saturated or unsaturated, will brand the states overweight. A balanced healthy diet will keep the vital processes in our bodies to function efficiently to maintain a salubrious body.
Source: https://www.aplustopper.com/fats-oils/
Posted by: cappssomay1959.blogspot.com

0 Response to "Both Animal Fats And Plant Oils Are Examples Of What Monomer?"
Post a Comment